The NTP protocol broadcasts a time information within a network in order to make sure that all clocks on a network are synchronised with an acceptable offset. NTP is one of the first protocols to be introduced and it has met a great success. NTP is easy to implement since it operates on the Internet network and since there are public servers available to retrieve the time.
Using the Internet as a support network for this protocol features many advantages but also drawbacks, such as the fact to expose servers to external attacks (DDoS attacks for example). This type of attack can entirely paralyse a network and have a significant impact on the activity of a company.
It is paramount to know all the possibilities the NTP protocol offers in order to configure a network in an optimal way. As a result, an appropriate configuration not only enables to make the most of the advantages of NTP, but also to protect against potential attacks.
The different operating modes of the Network Time Protocol
In order to have the best protection possible, it is important not to rely on public NTP servers, but rather to design a network autonomously by achieving synchronisation with a reliable time server via a reference source such as GPS.
NTP can operate in various ways:
- Unicast: This is the standard operating mode of NTP, in which the client periodically sends a timestamp request to the servers to which it is connected, in order to synchronise its clock.
- Broadcast: In this case, synchronisation is not being carried out by clients but rather by servers which periodically send their timestamps on the network. Clients subscribing to the servers can use the timestamps received in order to synchronise their clock.
- Multicast: The multicast mode is a variant of the broadcast mode, in which servers do not send their timestamps to the entire network but to a specific multicast address. This mode slightly reduces network load but requires network equipment capable of handling multicast.
- Manycast: This new mode has been introduced with NTPv4. This is a variant of the multicast mode, in which clients find the nearest servers available using a dedicated mechanism. Once they found the servers, clients will connect to them via unicast. By strategically distributing the servers in the network, it is possible to distribute the load of each server to optimise the network.
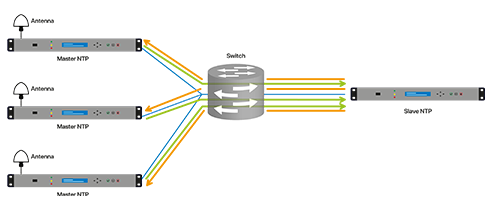
This is the most recent broadcasting mode which has been designed to be the most effective. This is the broadcasting mode to be used when one is equipped with the appropriate hardware. All equipment must handle NTPv4.
Whatever the timestamping broadcasting mode, it is important to secure your network to protect against attacks.
A well-known and documented vulnerability relates to NTP control messages, better known as mode 6. Indeed, if communications on the network are not authenticated, it is possible to retrieve many information or to initiate an amplification attack within the NTP network. NTP servers must be updated to a corrected version which allows for protection and deactivation of control messages in order to ensure complete immunity against this vulnerability.
One of the best practices when configuring an NTP network is to secure exchanges by authenticating all communications. This avoids that hackers impersonate a machine on the network. Authenticating NTP messages on the network enables to protect against a wide range of attacks. This function is activated by default on recent devices.
In order to protect against the potential corruption of some servers, NTP servers can be paired. This “peer-to-peer” operating mode enables NTP devices to act both as client and server. This can be useful to detect the offset of a server.
Whatever the operating mode and measures implemented to counter attacks, it is paramount to supervise your network to be informed in case of suspicious activity and react as quickly as possible. There are several solutions available to supervise a time network. It is important to be able to detect significant disruption of one of several clocks as early as possible. Monitoring the NTP traffic of your network enables to easily track any suspicious traffic before it can have a negative impact.
In general, is it best to follow the Best Current Practices (BCP 38, introduced in the RFC2827) to protect against DDos attacks. The RFC 8633 features the best practices to be implemented for the NTP protocol in terms of safety, for example.
Thinking about the configuration of your NTP network beforehand is necessary in order to make the most of this protocol and achieve efficient, secure time synchronisation. If some precautions are observed and the appropriate safety measures are implemented, it is then possible to protect against most attacks (including distributed denial-of-service attacks) and achieve a high-quality time synchronisation with optimised resource costs.
With over 150 years of expertise in time management and present in more than 140 countries, Bodet Time is a major French leader in time synchronisation and time frequency. Installing a Netsilon NTP time server locally allows for achievement of reliable time synchronisation and strengthened computer network.

