Time synchronisation is of paramount importance for industrial applications of many sectors. The energy sector is no exception. Using an accurate and reliable time is necessary for greater reliability and security, to anticipate and prevent breakdowns, bill consumption, as well as to test and check the proper operation of protection devices in energy production and management systems.
The importance of time synchronisation in energy management
Time synchronisation plays a central role in the management and operation of modern electricity networks. Indeed, it is required that time is highly accurate for several critical operations:
- Coordination: Network operators use synchronised clocks to coordinate all operations across the network. For example, the triggering of protection relays in the event of a fault must be accurate down to milliseconds to isolate the damaged part of the network without affecting others.
- Analysis: When an unexpected event occurs, its analysis will require accurate timestamps. Sensors record data on fluctuations and interruptions, thus enabling engineers to determine the cause of a breakdown or an abnormal event by using time information.
- Management: Energy providers use management systems which require accurate time synchronisation for several tasks such as billing as well as optimisation of energy distribution and consumption. This helps to reduce losses and improve overall network efficiency.
Main synchronisation techniques
Time distribution will rely on several technologies and protocols in order to provide accurate synchronisation. The most widely used include:
- GPS (Global Positioning System): GPS synchronised clocks are often used in electricity networks to provide an accurate reference time. GPS offers an accuracy down to microseconds, which is sufficient for most energy applications. The GPS system is based on a constellation of satellites and a set of terrestrial receivers, with the satellites transmitting signals containing data on their precise location and time. GPS is available worldwide and equivalent systems have been developed by several state actors.
- PTP (Precision Time Protocol): The PTP defined by the IEEE 1588 standard is able to synchronise clocks on a local network with great accuracy. It is especially useful in environments where highly accurate synchronisation is required (breakdown analysis, for example). PTP is available in many time server models. For example, the IEC61850 9-3 and IEEE C37.238 PTP profiles ensure optimum reliability and interoperability for power generation systems.
- NTP (Network Time Protocol): Although it provides less accuracy than PTP, NTP is widely used for synchronising clocks on a computer network. It offers sufficient accuracy for many industrial and commercial applications. NTP is a UDP-based protocol, defined in its latest version (4) by the RFC 5905. A simplified version of NTP is available and known as SNTP (for Simple NTP).
- IRIG: IRIG time codes have been developed by the Inter-Range Instrumentation Group and are widely used in both military and civil applications. The IRIG-B code is especially used in the context of electricity distribution.
None of these techniques is better than the others: each one features its advantages and its requirements. Some of them include:
- Interference problems: This is a particular challenge for GPS signals, which can be disrupted by atmospheric conditions or deliberate interference. To alleviate this issue, time distribution systems often incorporate redundant time sources as well as error correction algorithms (see our article on that matter).
- Excessive latency: Latency in communication networks can affect synchronisation accuracy. A protocol such as PTP makes up for this latency by continually adjusting clocks according to the delays observed. It is then necessary to be equipped with suitable time servers and hardware.
- Physical damage to equipment: Clocks and synchronisation devices must be robust and reliable to operate in “hostile” industrial environments. Since accidental breakdowns and damage are unavoidable, a principle of redundancy must be used when designing synchronisation systems. A protocol such as NTP is particularly suited to this context, with the use of a robust reference clock as time source.
Example of applications in the energy sector
Here are a few examples of real applications, one for each major aspect of the energy sector (coordination, analysis and management).
- Coordination: synchrophasors. Behind this strange name lie phase measurement units which, coupled with the GPS system, make it possible to map power flows in an electricity network several dozen times a second. These measurements are essential for creating smart grids.
- Analysis: reconstruction of events. Most of the time, the electricity distribution network operates faultlessly. But sometimes, a breakdown occurs and can be followed by a cascade of breakdowns and malfunctions. This is what happened in North America in 2003, costing nearly 6 billion dollars. To trace back the chain of events and implement corrective measures for the future, a time reference common to all events is required.
- Management: billing. Most providers’ rates vary according to the time of day (concept of off-peak hours). To guarantee accurate billing in this context, it is necessary to be equipped with accurate clocks.
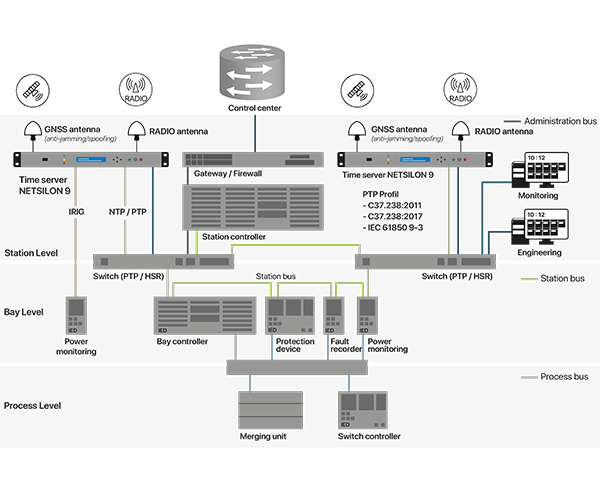
Time distribution in the energy sector is a critical component for ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of modern electricity networks. Nowadays, there are all kinds of technical solutions available to ensure efficient time management in this context. The most difficult for organisations is to choose the technologies best suited to their needs.
With over 150 years of expertise in time management and present in more than 140 countries, Bodet Time is a major French leader in time synchronisation and time frequency. Netsilon NTP and PTP time servers provide a reliable and accurate reference time meeting the needs of the energy sector.
Do you have the project of securing time information in the energy sector?

